153월2024
업계 리뷰
댓글: 댓글 없음.
현금 거래는 인쇄, 운송, 보관 및 돈 계산과 같은 지불 활동을 조직하는 데 드는 비용을 포함하여 다양한 단점이 있습니다. 게다가 현금 거래는 종종 대규모 거래에서 세금 회피에 악용되고 도난, 위조 통화 및 자금 세탁과 같은 사회 보장 관련 문제를 일으킵니다. 이러한 과제에 대응하여 현금 사용에 대한 제한이 도입되었고 비현금 지불 추세가 점점 더 인기를 얻고 있습니다.
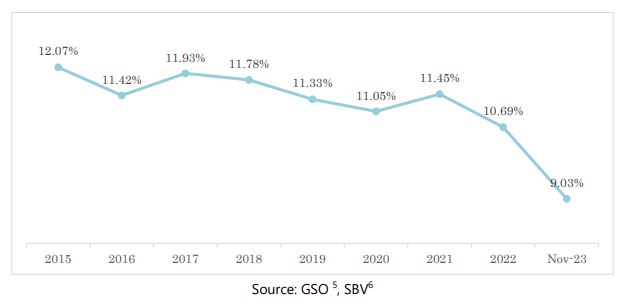
현금 결제 비중을 총 결제 수단에서 줄이기 위한 노력은 2016년부터 결정 2545/QD-TTg(2016~2020년 베트남 비현금 결제 개발 프로젝트)에 따라 시행되기 시작했습니다. 그러나 사람들이 직접 접촉을 제한해야 했던 코로나19 팬데믹 기간 동안 결제 행동에 상당한 변화가 있었습니다. 이러한 노력에도 불구하고 2020년 말까지 현금 결제 비중을 10% 미만으로 줄이겠다는 목표는 달성되지 않았으며 2021년에는 증가하는 경향이 있었습니다 [1] . 또한, 은행 및 지불 처리 소프트웨어와 솔루션 제공을 전문으로 하는 미국의 기술 회사인 Fidelity National Information Services(FIS)가 온라인 및 오프라인 매장에서 쇼핑할 때의 소비자 지불 추세 보고서에 따르면, 베트남의 개인 거래에서 현금 지불의 비중은 2022년에도 높은 수준을 유지했습니다. 베트남은 47%의 비율로 태국(56%)과 일본(51%)에 이어 아시아 지역에서 3위를 차지했습니다. [2] 특히 농촌 및 외딴 지역의 민간 거래와 건강 및 교육 분야의 비현금 지불은 약간의 변화를 보였지만 비교적 적은 수준을 유지하고 있습니다. [3] 비현금 거래 증가를 더욱 촉진하기 위해 정부는 2021-2025년 기간 동안 무현금 결제 개발 프로젝트(2021년 10월 28일 발행된 결정 번호 1813/QD-TTg)와 2030년을 목표로 하는 2025년까지 은행 부문 디지털 전환 계획 [4] (2021년 5월 11일 발행된 결정 번호 810/QD-NHNN)을 계속 시행하고 있습니다. 현금 결제 비율을 10% 미만으로 줄이겠다는 목표는 2022년 10월(9.78%)에 달성되었고, 2023년에는 꾸준히 감소하여 2023년 9월에 가장 낮은 비율(8.53%)을 기록했습니다.
2015-2021년 총 지불수단 중 현금 비중(%)
비현금 결제는 이점과 발전에도 불구하고, 몇 가지 위험에도 직면합니다. 개인 계좌 정보 유출과 같은 첨단 사이버 범죄 및 은행 계좌 침해를 수반하는 사기 행위가 위험에 포함됩니다. 은행들은 인공지능을 활용하여 고객의 보안을 강화하고 새로운 형태의 사기에 대응할 수 있도록 다양한 기술 솔루션을 도입하고 있지만, 이는 여전히 지속적이고 진화하는 과제입니다. [8] 현금 결제를 완전히 대체할 수는 없으며, 두 결제 방식은 앞으로도 계속 공존할 것입니다.
비앤컴퍼니
이 기사는 ASEAN Economic News의 칼럼 “베트남 트렌드 읽기”에 게재되었습니다. 자세한 내용은 아래를 참조하세요.
|
주식회사 비앤컴퍼니 2008년부터 베트남에서 시장 조사를 전문으로 하는 최초의 일본 기업입니다. 업계 보고서, 업계 인터뷰, 소비자 설문 조사, 비즈니스 매칭을 포함한 광범위한 서비스를 제공합니다. 또한, 최근 베트남에서 900,000개 이상의 기업에 대한 데이터베이스를 개발하여 파트너를 검색하고 시장을 분석하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다. 문의사항이 있으시면 언제든지 문의해주세요. info@b-company.jp + (84) 28 3910 3913 |
다른 기사를 읽어보세요
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]