12Mar2025
Latest News & Report / Vietnam Briefing
Comments: No Comments.
Ho Chi Minh City, one of the largest urban centers in Vietnam, is taking significant steps toward improving its waste management system. With the recent announcement of a VND 3,500 billion waste incineration plant aimed at generating electricity, the city is addressing the urgent challenges posed by increasing household waste. This article will explore the current situation of household waste in Ho Chi Minh City, the methods used for waste treatment, the new movement toward waste-to-energy solutions, and the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead.
The Current Situation of Household Waste in Ho Chi Minh City
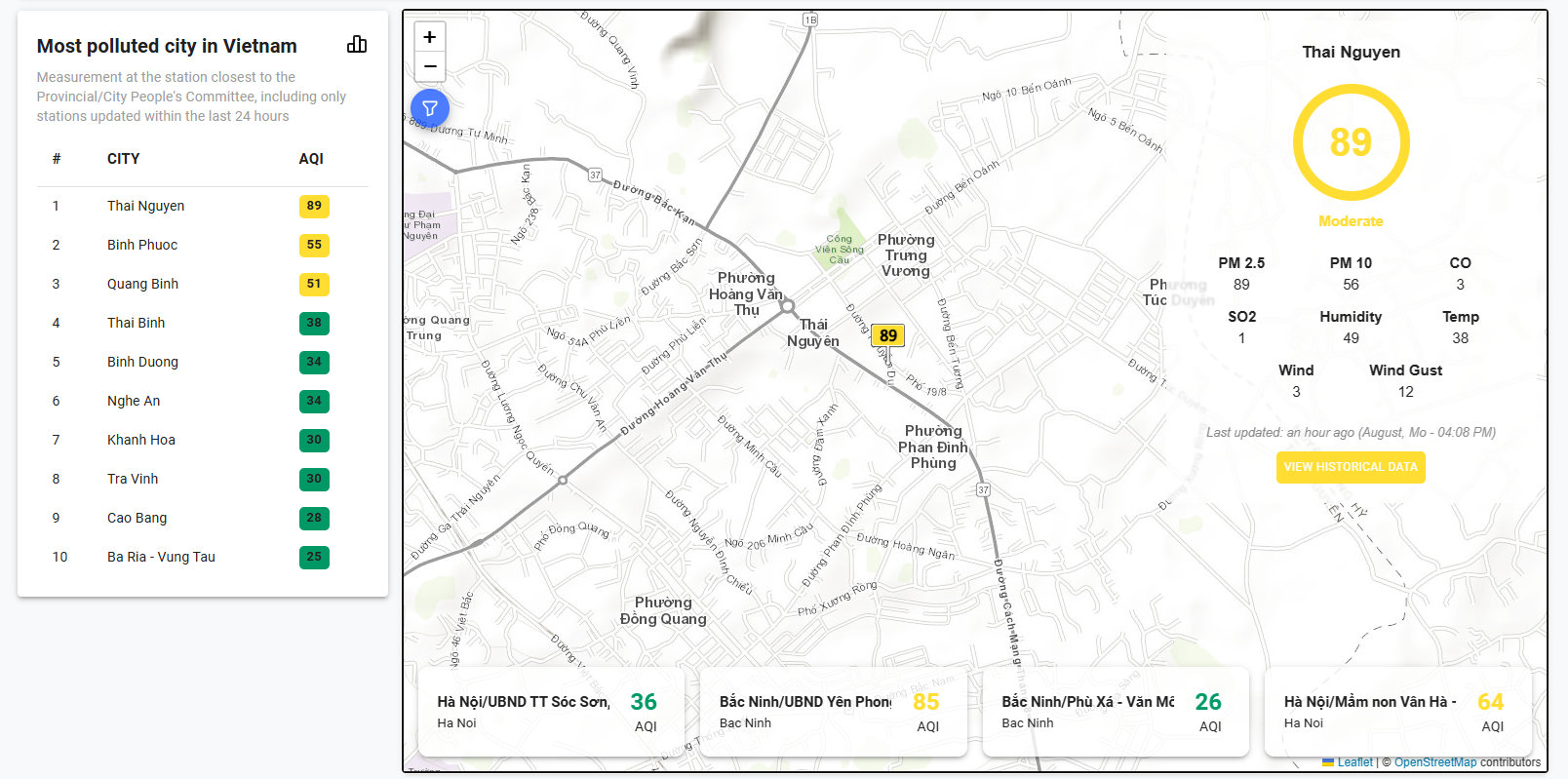
Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC), Vietnam’s largest and most densely populated urban center, is home to over 9 million people. With rapid urbanization and economic growth, the city generates an average of 13,000 tons of domestic solid waste per day as of 2024. Of this, approximately 10,000 tons are recycled or treated daily. Since 2020, the volume of household waste has increased by around 5.6% annually, though the growth rate has slowed in recent years. [1]
The composition of household waste in HCMC is primarily organic matter (50–60%), while recyclable materials such as plastic, paper, and rubber make up only 27% at waste treatment facilities. Currently, the city relies on two main waste treatment methods: landfilling (69%) and recycling/composting (21%), while 10% of waste is incinerated [2]. The continued reliance on landfills has raised concerns over environmental pollution, land scarcity, and inefficient resource recovery. Additionally, despite efforts to improve waste classification at the source, a large portion of waste remains mixed, making it difficult to process effectively. The growing waste volume and strained collection and transportation systems highlight the urgent need for more sustainable and advanced waste management solutions.
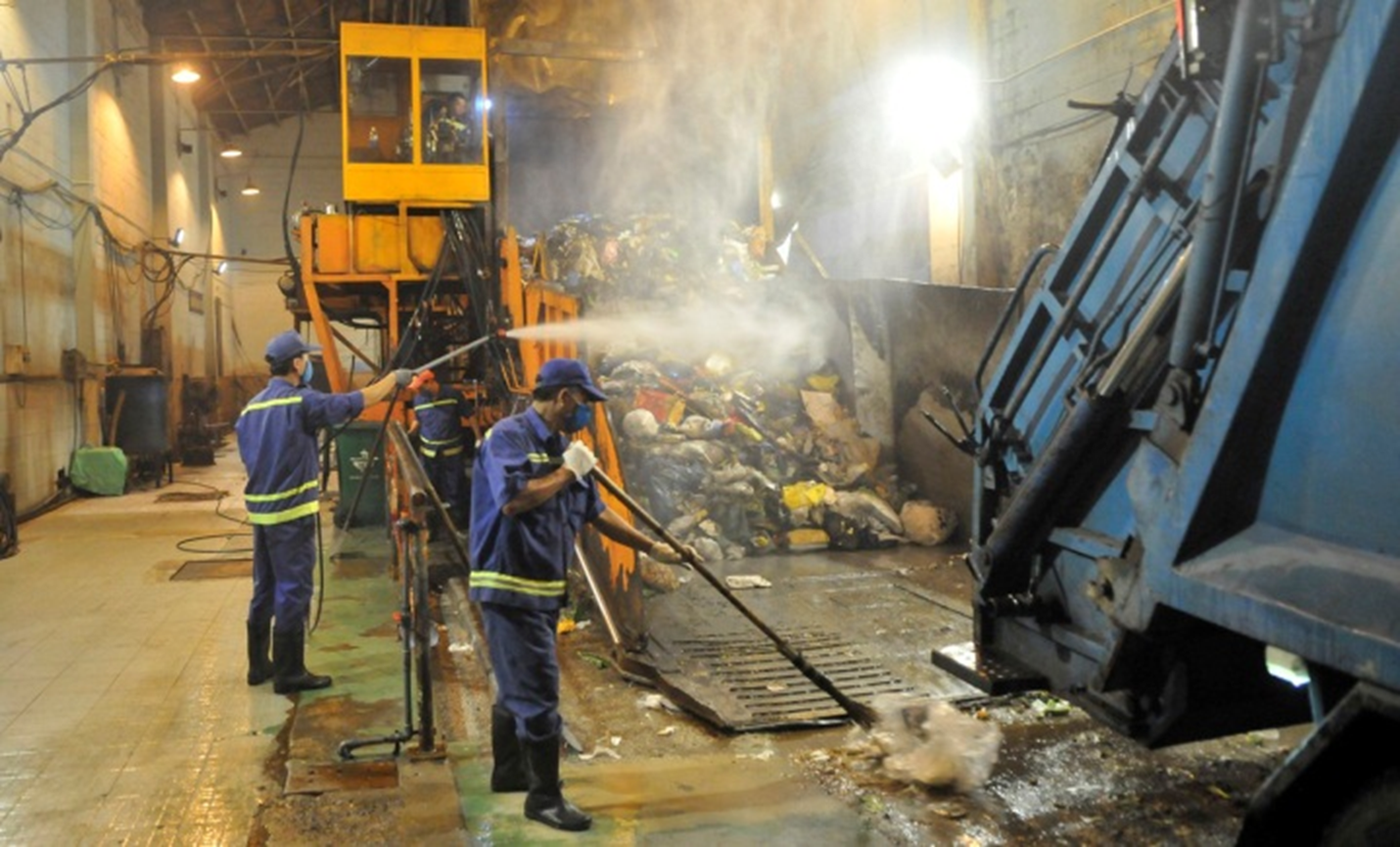
Domestic waste treatment at Ho Chi Minh City Urban Environment Company Limited
Source: tapchimoitruong.vn [3]
The Movement of Waste Treatment to Generate Electricity
Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC) is actively shifting toward waste-to-energy (WTE) technology as part of its broader waste management strategy. Since 2020, the City Party Committee and People’s Council have set a policy target: by 2025, at least 80% of domestic waste should be treated using modern technologies like waste incineration for electricity generation and recycling, with the goal of reaching 100% by 2030. This transition aligns with Resolution No. 98/2023/QH15 issued by the National Assembly on June 24, 2023, which guides the city’s waste treatment reforms. To implement this, the People’s Committee of HCMC has focused on two key solutions, (1) converting existing solid waste treatment technologies, (2) attracting investment in waste treatment projects under the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model [4].
To achieve its goal of modernizing waste treatment, Ho Chi Minh City has started construction on two waste-to-energy plants with a total treatment capacity of 4,000–4,600 tons per day. These facilities are expected to be completed by 2026, contributing to the treatment of a significant portion of the city’s domestic waste and reducing reliance on landfills.
Below is an overview of the two waste-to-energy plants under construction in Củ Chi – Ho Chi Minh city:
| Name | Start time | Expected Completion | Investor | Capital Scale (Mil USD) | Treatment Capacity (tons/day) | Power Generate capacity | Technology |
| Tâm Sinh Nghĩa WTE 6 | July 2024 | End of 2025 | Bamboo Capital Group & BCG Energy | 253 | 2,000–2,600 | 60MW | SUS-Hitachi Zosen Vonroll |
| Vietstar WTE [5] | March 2025 | Mid-2026 | Vietstar | 140 | 2,000 | 40MW | German Technology |
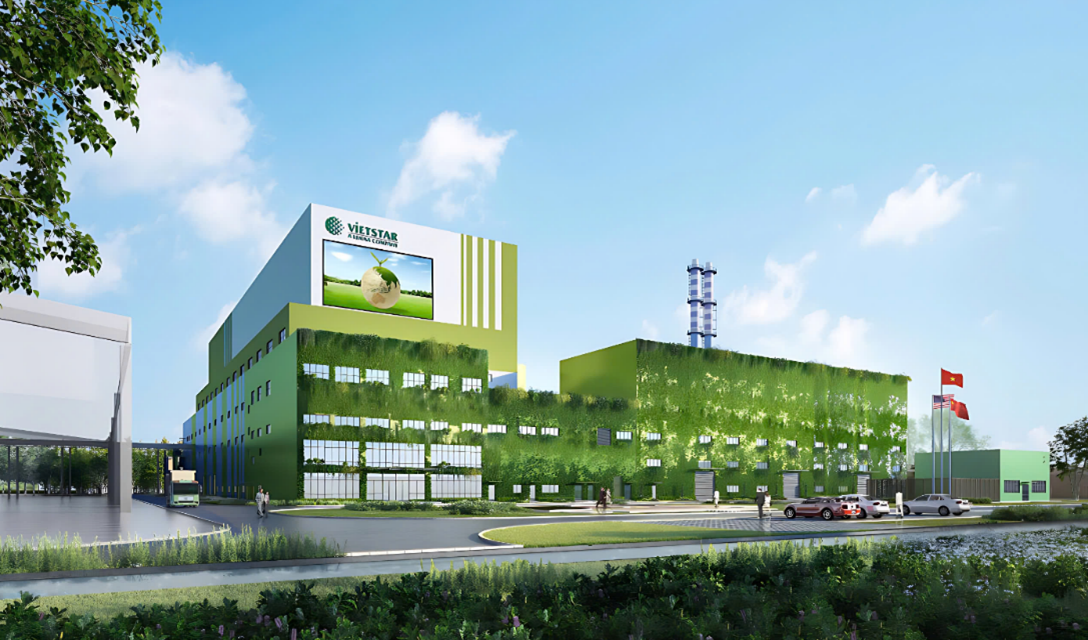
Vietstar waste-to-energy project
Source: Vietstar
Opportunities and Challenges for Waste Incineration to Generate Electricity
The decision to invest in a waste incineration plant presents both opportunities and challenges for Ho Chi Minh City. One of the key opportunities lies in the potential to meet the city’s growing energy demands through sustainable practices. By converting waste into electricity, the city can reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to its energy security.
Moreover, the incineration plant aligns with Ho Chi Minh City’s policies aimed at improving waste management and promoting sustainable development. The city has set ambitious goals to enhance waste treatment processes, reduce landfill usage, and increase recycling and composting rates. The establishment of the incineration plant is a crucial step toward achieving these objectives. However, one of the major obstacles remains the limited waste classification and collection at the source, which affects the efficiency of waste treatment and the quality of incineration processes. Without proper waste separation, non-combustible materials may enter the incineration system, reducing its effectiveness and increasing operational challenges.
The implementation of waste incineration also faces other challenges. Public perception and acceptance of incineration as a waste management method can be a significant hurdle. Concerns about air pollution and the potential health impacts of incineration must be addressed through comprehensive environmental assessments and transparent communication with the community.
Furthermore, the success of the incineration plant will depend on the efficiency and effectiveness of its operation. Ensuring that the facility meets environmental standards and utilizes advanced technologies will be critical in mitigating any negative impacts associated with waste incineration. Overcoming these challenges will require strong policy support, public awareness campaigns, and improvements in waste classification and collection systems to maximize the plant’s benefits.
Conclusion
The construction of HCMC’s new VND 3,500 billion waste incineration plant marks a crucial step in Vietnam’s transition toward sustainable waste management. With an increasing amount of household waste, the city can no longer rely solely on landfills. Waste-to-energy incineration presents a viable solution that not only reduces waste volume but also generates electricity, contributing to the city’s energy needs.
While challenges remain, including high investment costs and waste classification inefficiencies, the benefits of WTE incineration outweigh the drawbacks. By implementing supportive policies, advancing waste separation systems, and adopting modern incineration technologies, HCMC can establish a more sustainable waste management framework for the future. If successfully executed, this initiative could serve as a model for other cities in Vietnam seeking innovative solutions to their waste management crises.
[1] https://scem.gov.vn/vi/tin-tuc-trung-tam/tin-tuc/tp-hcm-phat-sinh-trung-binh-13-000-tan-chat-thai-ran-sinh-hoat-moi-ngay-1375.html
[2] https://scem.gov.vn/vi/tin-tuc-trung-tam/tin-tuc/tp-hcm-phat-sinh-trung-binh-13-000-tan-chat-thai-ran-sinh-hoat-moi-ngay-1375.html
[3] https://tapchimoitruong.vn/phap-luat–chinh-sach-16/T%C3%ACm-gi%E1%BA%A3i-ph%C3%A1p-%C4%91%E1%BB%99t-ph%C3%A1-trong-c%C3%B4ng-t%C3%A1c-qu%E1%BA%A3n-l%C3%BD-ch%E1%BA%A5t-th%E1%BA%A3i-r%E1%BA%AFn-sinh-ho%E1%BA%A1t-t%E1%BA%A1i-Th%C3%A0nh-ph%E1%BB%91-H%E1%BB%93-Ch%C3%AD-Minh-18425
[4] https://scem.gov.vn/vi/tin-tuc-trung-tam/tin-tuc/tp-hcm-phat-sinh-trung-binh-13-000-tan-chat-thai-ran-sinh-hoat-moi-ngay-1375.html
[5] https://vnexpress.net/tp-hcm-khoi-cong-nha-may-dot-rac-phat-dien-3-500-ty-dong-4857063.html
* If you wish to quote any information from this article, please kindly cite the source along with the link to the original article to respect copyright.
| B&Company
The first Japanese company specializing in market research in Vietnam since 2008. We provide a wide range of services including industry reports, industry interviews, consumer surveys, business matching. Additionally, we have recently developed a database of over 900,000 companies in Vietnam, which can be used to search for partners and analyze the market. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you have any queries. info@b-company.jp + (84) 28 3910 3913 |