215 月2025
最新消息及报道 / 越南简报
评论: 没有评论.
介绍
近年来,越南与日本的战略伙伴关系已从传统领域拓展至人工智能 (AI) 等前沿领域。两国企业秉持着数字创新和技术自力更生的共同愿景,不断拓展合作,将越南蓬勃发展的科技生态系统与日本先进的技术专长相融合。从合资企业、战略投资到培训项目和政府主导的举措,人工智能合作的势头正在改变两国经济。
政府支持和战略协调
政府层面的双边支持为人工智能合作奠定了坚实的基础。2003年启动的“越日联合倡议”已发展成为应对关键经济挑战的平台。该倡议的最新阶段(第八阶段)于2023年启动,重点关注数字化转型和人工智能融合。[1]越南国家数字化转型计划优先发展人工智能,通过定向资金、政策改革和能力建设举措来提升国家竞争力[2].
与此同时,日本的社会 5.0 愿景推动数字技术融入社会的各个方面[3]这些协调一致的国家战略支持公私合作、监管创新和基础设施建设。此外,日本贸易振兴机构(JETRO)和日本国际协力机构(JICA)等日本政府支持的机构也支持了众多旨在促进越南科技初创企业创新的举措,包括致力于人工智能、机器人技术和金融科技领域的企业。[4].
人工智能的商业合作和投资
在商业层面,越南与日本的人工智能合作已取得切实成果。越南领先的科技公司 FPT Corporation 宣布投资 14 亿美元建设一座人工智能工厂,该工厂将于 2024 年投入运营,利用英伟达先进的芯片和软件开发大型语言模型、生成式人工智能和自主系统。[5]此外,FPT还与大和控股等日本公司签署了谅解备忘录[6] – 一家领先的日本物流公司,以其先进的包裹递送和供应链解决方案以及 TradeWaltz 而闻名[7] – 一家日本初创公司,提供基于区块链的平台,数字化和简化国际贸易流程,共同创建人工智能物流解决方案、数据集成工具和云平台,旨在优化全球供应链和贸易运营。
与此同时,日本 NTT 数据集团旗下的子公司 NTT Data Vietnam 为越南和亚洲各地的客户提供 IT 服务和数字转型解决方案,目前正与越南软件公司合作,打造人工智能驱动的商业智能工具[8] 并与当地大学合作开展专注于智慧城市技术和医疗保健解决方案的研发项目。
人才发展与知识转移
劳动力发展是越南与日本此次合作的重要支柱。专注于数字保障和软件测试的日本公司 AGEST Inc. 成立了 AGEST 越南公司,旨在弥补数字工程和人工智能开发领域的人才缺口。AGEST 越南公司与 20 多所越南大学合作,协助设计课程并提供机器学习、网络安全和云计算等关键领域的认证项目。其目标是打造一条人才输送管道,使越南企业和面临科技领域劳动力短缺的日本企业都能从中受益。[9].
这些举措是对更广泛的教育伙伴关系的补充,例如日本国际协力机构 (JICA) 与越南机构合作推广 STEM(科学、技术、工程和数学)教育[10]奖学金、实习和交流项目也增加了,让越南学生有机会接触日本的人工智能研究环境 [11].
案例研究:人工智能在行动
a. 教育
人工智能应用合作的一个显著例子是 阿卡特斯,一款由越南 FPT 公司开发的人工智能翻译工具。AkaTrans 使用经过数百万句对训练的神经机器翻译模型来提高日越翻译的准确性,尤其是在 IT 相关文档的翻译中。该工具最初旨在协助为日本客户开展项目的工程师和翻译人员,旨在弥合科技领域的语言差距,并增进两国在贸易、教育和旅游方面的交流。[12].
b. 医疗保健领域
日本资助的越南人工智能项目正在利用创新诊断技术提升医疗保健行业。这些工具利用人工智能进行图像分析,帮助医生更早、更准确地发现癌症等疾病。一个值得注意的例子是Nura健康检查模型,这是T-松冈医疗中心与富士胶片合作开发的,提供快速精准的健康筛查,包括癌症检测。[13]该模式已在河内、岘港等越南主要城市的医院进行测试。
 |
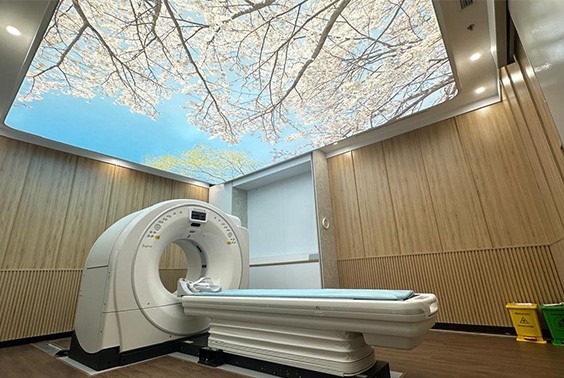 |
| 新 NURA 的入口 来源: 富士胶片 |
NURA 新安装的 CT 扫描仪 来源: 富士胶片 |
c.农业
日本率先在农业领域推出人工智能应用,例如可以预测害虫爆发以减少农药使用的智能手机应用程序[14]越南正在采用类似的人工智能技术来提高农业效率和可持续性。例如,湄公河三角洲的农民正在使用无人机进行精准施肥,这不仅节约了资源,还降低了劳动力成本。这些创新技术目前正在越南推广,湄公河三角洲等地区的农民正在采用类似的人工智能工具来提高农业效率和可持续性。
在越南,类似的人工智能技术正在被采用,以提高农业效率和可持续性。例如,湄公河三角洲的农民正在使用无人机进行精准施肥,这不仅节约了资源,还降低了劳动力成本。此外,人工智能系统也被用于水产养殖,例如超集约化虾类养殖,以监测环境条件并优化生产。
挑战与未来之路
尽管取得了这些积极进展,挑战依然存在。语言和文化差异可能会使协调工作更加复杂。越南城乡之间存在数字鸿沟,这可能会阻碍人工智能工具的广泛应用。此外,日本传统上对企业变革的保守态度有时会减缓联合创新的步伐。然而,长期前景仍然非常乐观。随着越南继续吸引外国直接投资进入高科技领域,以及日本寻求实现供应链和人才来源多元化,人工智能合作很可能成为双边关系的核心支柱。建立更多以人工智能为重点的商务代表团、创新中心和跨境孵化器可以进一步加速进展。增加政府对双边研发的资助,再加上为在两国开展业务的人工智能初创企业提供新的激励措施,也将有助于保持发展势头。
结论
越南与日本企业在人工智能领域不断拓展的合作,彰显了两国的战略远见和互信。从工业人工智能应用到教育合作和政策协调,这一伙伴关系不仅推动着……在政府、大学和企业的大力支持下,越南和日本已准备好共同打造一个造福两国公民、企业乃至整个亚太地区的人工智能生态系统。
[1] https://vietnamnews.vn/economy/1689178/viet-nam-japan-joint-initiative-undergoes-mid-term-review.html
[2] https://vietnamlawmagazine.vn/maximum-support-for-data-industry-to-turn-vietnam-into-digital-nation-party-chief-73807.html
[3] https://vju.ac.vn/en/japans-society-5-0/
[4] https://vir.com.vn/inno-vietnam-japan-fast-track-pitch-2023-comes-to-hanoi-106121.html
[5] https://www.reuters.com/technology/vietnams-fpt-invest-200-mln-ai-factory-using-nvidia-chips-2024-04-23/
[6] https://english.thesaigontimes.vn/fpt-partners-with-japanese-firms-to-boost-digital-transformation/
[7] https://www.tradewaltz.com/en/news/1361/
[10] https://www.jica.go.jp/english/overseas/vietnam/activities/index.html
[11] https://vietnamnews.vn/society/1689873/japan-to-offer-scholarships-for-vietnamese-students.html
[12] https://fptsoftware.com/newsroom/news-and-press-releases/news/akatrans-an-it-translation-tool-using-ai-developed-by-fpt
[13] https://www.fujifilm.com/vn/en/news/hq/11563
[14] https://dig.watch/updates/japanese-farmers-turn-to-ai-to-combat-pests?utm_source=chatgpt.com
*如果您想引用本文中的任何信息,请注明来源以及原始文章的链接,以尊重版权。
| B&Company
自 2008 年以来,日本第一家专门从事越南市场研究的公司。我们提供广泛的服务,包括行业报告、行业访谈、消费者调查、商业配对。此外,我们最近还开发了一个包含越南 900,000 多家公司的数据库,可用于搜索合作伙伴和分析市场。 如果您有任何疑问,请随时与我们联系。 信息@b-company.jp + (84) 28 3910 3913 |