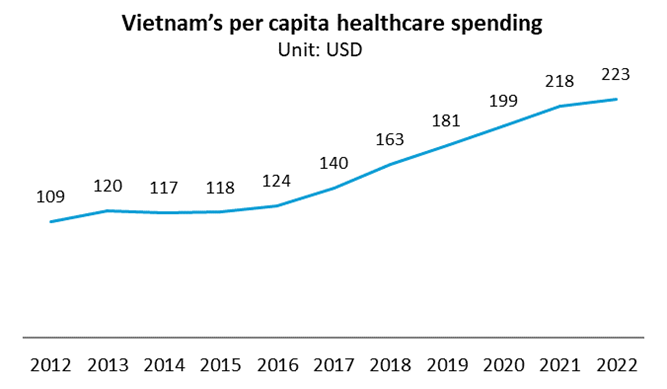
Vietnam’s economic transformation is reshaping its position as a leading destination for foreign investment. In 2024, the country attracted nearly $25 billion in FDI, a 9% year-on-year increase – a strong signal of confidence in the Vietnam industry sector. Pro-business policies, strategic funds such as the $400 million support package for semiconductor manufacturing, and long-term initiatives like the Logistics Development Strategy 2025–2035 further highlight the government’s commitment to creating a competitive investment climate.
This article identifies high-potential Vietnam industry sectors, including Information Technology & AI, Renewable Energy, Healthcare, Semiconductors, Electric & Hybrid Vehicles, and Logistics. Also, this guide explores each Vietnam industry sector with insights on the current landscape, development outlook, government incentives, and key investment cases, primarily based on research from B&Company.
.