Vietnam has become a pivotal player in global manufacturing, with its electric and electronic (E&E) industry emerging as a cornerstone of its economic growth. The industry’s rapid expansion has been fueled by the establishment of production facilities by major multinational corporations such as Samsung, Intel, Foxconn, etc, attracted by the country’s competitive labor costs, strategic geographical location, and supportive government policies. To maintain its competitive edge and adapt to the fast-paced nature of the global market, Vietnam has increasingly turned to industrial robotics, which provides essential advantages in efficiency and precision for the production of electronic components and devices.
Current Situation
In recent years, the use of industrial robotics has become more prevalent within Vietnam’s E&E industry, particularly among large multinational corporations. These companies, such as Samsung, LG, Panasonic, and Intel, have heavily invested in advanced robotic systems at their Vietnamese manufacturing plants.
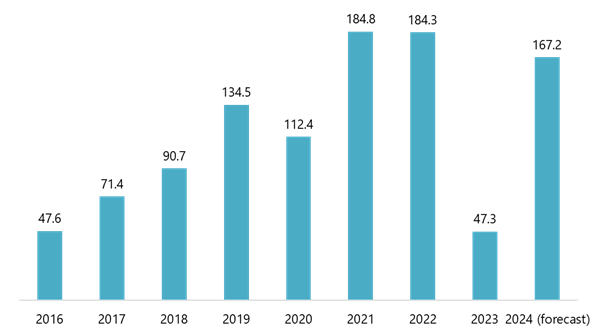
Despite these advances, Vietnam’s robotics market remains relatively underdeveloped compared to countries with more mature robotics industries. According to Statista, electric/electronic industry robotics dominates the industrial robotics market in Vietnam, even though it suffered with a heavy decrease in 2023, the market is projected to have a revenue volume of USD 167.20 million in 2024[1].
Revenue from Robotics in the Electric/Electronic Industry (2016-2024)
Unit: million USD
Source: Statista
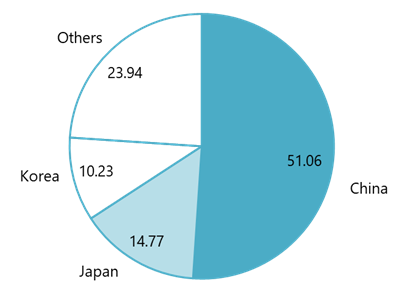
The majority of robots in use within Vietnam’s E&E industry are imported, mainly from China, Korea and Japan, all of which have established reputations for robotics manufacturing. The chart below shows the percentage of imported industrial robots to Vietnam in 2022.
Percentage of industrial robots imported to Vietnam (2022)
100% = 175.81 thousand USD
Source: ICT Trade Map
Key Players
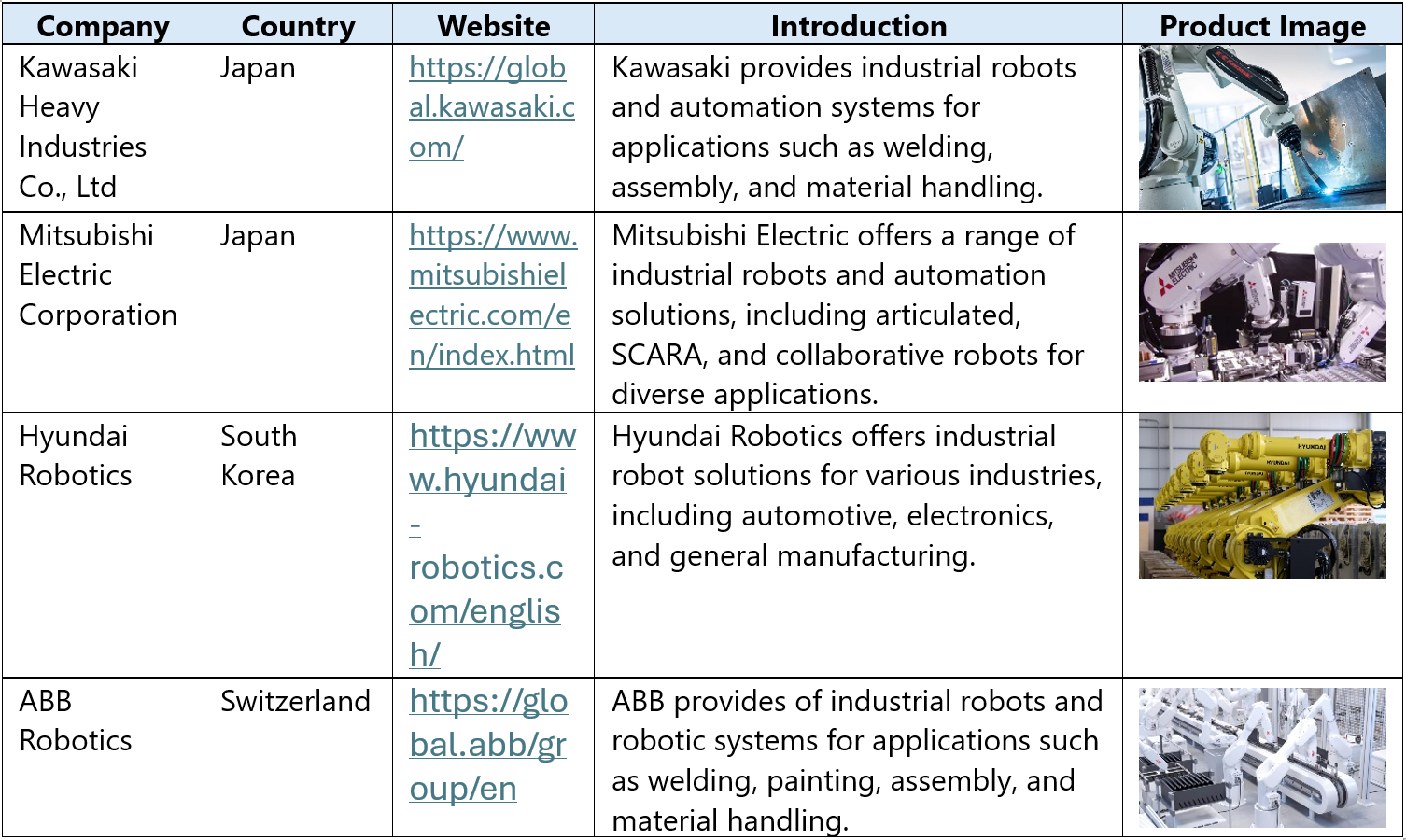
In Vietnam’s industrial robotics sector, the domestic market is primarily dominated by foreign brands, capturing significant market share. These companies offer advanced, high-quality robotic solutions tailored to meet the demands of Vietnam’s rapidly growing manufacturing industries, particularly in electronics, automotive, and textiles. While a few Vietnamese firms are emerging in the field, they remain in the early stages of development and often focus on assembling imported components rather than full-scale manufacturing.
The table below highlights some of the key players in Vietnamese industrial robot manufacturing industry
Source: B&Comany’s synthesis
This reliance on imported technology illustrates the lack of local robotics development capacity but also signals the Vietnamese government’s commitment to advancing industrial capabilities. Initiatives such as the “Made in Vietnam 4.0” strategy emphasize the importance of integrating advanced technologies, including robotics, into manufacturing to propel the country toward Industry 4.0. In addition to policy support, educational institutions in Vietnam have started to play a role in preparing the future workforce for a technology-driven economy. However, the current pool of workers trained in these fields remains small, and the country continues to depend on foreign technicians to install, maintain, and operate advanced robotic systems. This reliance on external expertise underscores a significant skills gap in the local labor market, which hinders the development of a self-sustaining robotics industry in Vietnam.
Growth Potential
Despite these challenges, the potential for growth in industrial robotics within Vietnam’s E&E industry is substantial. The electronics industry accounts for about 17.8% of Vietnam’s manufacturing industry, according to data from the General Office of Statistics as of 2023. A number of major electronics firms have relocated at least part of their supply chain to Vietnam in recent years. Notably, LG’s smartphone production has moved entirely from South Korea to Hai Phong. Apple has moved part of the production of its AirPods, while Nintendo has also transferred a part of its Switch Lite game console to Vietnam. Furthermore, key Apple supplier Foxconn was approved earlier this year to invest in two new facilities in Vietnam to the tune of USD 246 million[2]. Global demand for electronics, including consumer electronics, smart devices, and telecommunications equipment, is projected to continue rising over the next decade.
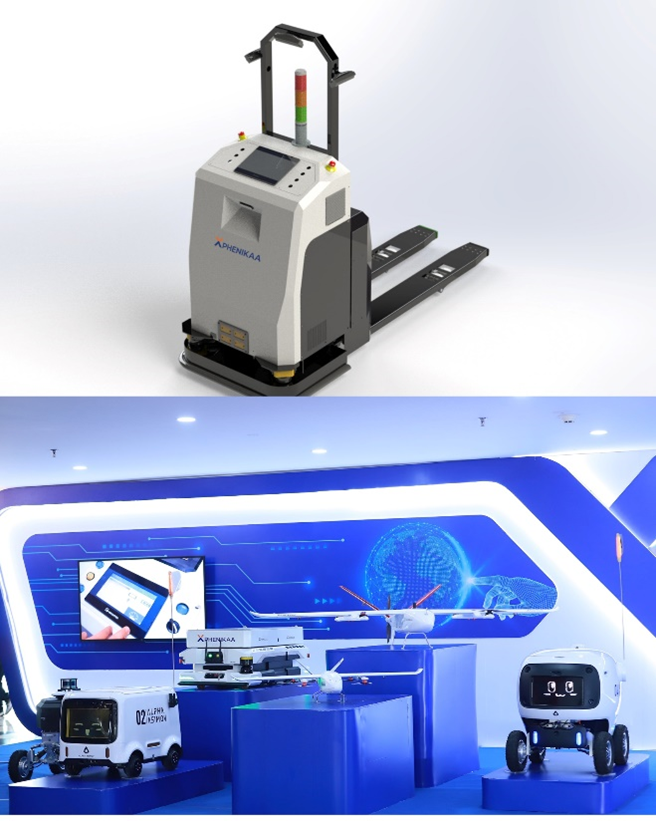
Recently, Phenikaa-X JSC (a member of Phenikaa Group) – a leading provider of “Make in Vietnam” intelligent automation (IA) robot solutions – officially supplied intelligent automation robots to the Samsung Electronics Thai Nguyen Factory (SEVT). With this, SEVT has become Samsung Electronics’ first factory globally to implement the AMR Pallet Mover robot in operations, assisting workers with heavy tasks and contributing to cost optimization and improved production and business efficiency[3].
Remaining Challenges
Despite the progress made in integrating robotics into Vietnam’s E&E industry, significant challenges remain. Firstly, the high cost of adopting robotic systems. Consequently, access to robotics in Vietnam’s E&E industry is largely limited to multinational corporations with extensive resources, while local firms may struggle to compete due to their limited access to automation.
Secondly, Vietnam’s reliance on imported robotics technology, which has resulted from the country’s limited capacity for local robotics manufacturing and innovation. Vietnamese companies currently depend on international suppliers for robotics equipment, which increases operational costs and poses supply chain risks, as spare parts, upgrades, and maintenance services must often be sourced from foreign providers.
Thirdly, the skills gap within the Vietnamese labor force is also a significant challenge. While universities and technical schools have begun to offer courses in robotics and automation, the level of training available still falls short of industry demands. Foreign specialists are frequently required to manage advanced robotics systems, which drives up costs and restricts local skill development
Finally, integrating robotics into existing production lines presents logistical and operational challenges. Many of Vietnam’s manufacturing facilities were not initially designed with automation in mind, so retrofitting these spaces to accommodate robotics can require significant adjustments in layout, infrastructure, and workflows. Older facilities may lack the technological foundation needed to support robotics, making integration complex and costly. For companies with outdated infrastructure, the shift to automation necessitates substantial reorganization, which can disrupt production and strain resources.
Sample image of AMR Pallet Mover robot from Phenikaa-X which was used by Samsung
Source: Phenikaa-X
Conclusion
The adoption of industrial robotics in Vietnam’s electric and electronic industry presents a promising avenue for enhancing productivity, improving quality, and meeting the demands of an expanding global market. Although Vietnam has made strides in incorporating robotics into its E&E sector, particularly within multinational corporations, several challenges continue to impede the widespread use of robotics. High costs, limited local expertise, reliance on foreign technology, and difficulties in adapting older facilities for automation are notable obstacles. Nevertheless, the growth potential for industrial robotics in Vietnam’s E&E industry is considerable. With rising global demand for electronics, increasing adoption of smart manufacturing under Industry 4.0, and strong government support, Vietnam has an opportunity to strengthen its position in the global E&E market.
[1] Statista (2024). Industrial Robotics – Vietnam. <Assess>
[2] Vietnam Briefing (2023). Vietnam’s Electronics Industry: A Guide to Emerging Opportunities. <Assess>
[3] Phenikaa Press Release (2024). The first Samsung Electronics factory globally to implement Phenikaa-X’s AMR Pallet Mover robot solution. <Assess>
| B&Company, Inc.
The first Japanese company specializing in market research in Vietnam since 2008. We provide a wide range of services including industry reports, industry interviews, consumer surveys, business matching. Additionally, we have recently developed a database of over 900,000 companies in Vietnam, which can be used to search for partners and analyze the market. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you have any queries. info@b-company.jp + (84) 28 3910 3913 |
Read other articles