Overview of the Rooftop Solar Power Situation in Vietnam
Vietnam is increasingly recognized as a rising star in the renewable energy sector, particularly in solar power. Solar radiation in Vietnam is also considered an infinite energy source. The average solar radiation can reach about 3-5 kWh/m² per day, with an average of 2,500 to 3,000 hours of sunshine per year. Vietnam can also install solar panels in various regions, including coastal areas, on lakes, in the plains, mountainous regions, and on rooftops, etc[1]. As of the end of 2022, Vietnam’s power system had a total installed capacity of 80,704 MW, of which solar power accounted for approximately 16,567 MW, making up about 20.5% (with over 9,000 MW coming from rooftop solar). By 2030, the Vietnamese government aims to reach 20.6 GW of solar power capacity, indicating a clear commitment to harnessing this renewable resource[2].
Rooftop solar power offers a unique advantage in Vietnam’s densely populated urban areas, where space for ground-mounted solar farms is limited. Residential and commercial buildings provide ideal locations for solar panels, helping to mitigate energy consumption and reduce electricity bills. This potential is particularly pronounced in urban centers like Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi, where energy demand is rapidly increasing. As the country continues to urbanize, rooftop solar installations can play a crucial role in meeting growing energy needs while promoting sustainable practices.
Workers working on rooftop solar panels in Vietnam
Ministry of Trade press release (Source)
Government Policies and Support
The Vietnamese government has demonstrated a strong commitment to renewable energy development, particularly through its policies and regulatory frameworks. The introduction of FiTs in through Decision 11/2017/QĐ-TTg[3] was a significant milestone, providing attractive rates for solar energy producers. Under these tariffs, rooftop solar power generated and fed back into the grid is compensated at a fixed rate, ensuring a stable return on investment for homeowners and businesses.
In addition to FiTs, the government has set ambitious targets for renewable energy development, more prominently in Decision 500/QĐ-TTg, or the 8th Power Development Plan (PDP VIII). The plan outlines that Vietnam’s solar power potential is approximately 963,000 MW and estimates that from now until 2030, the total capacity of solar power sources is expected to increase to 967,100 MW. The goal for 2050 is to raise total capacity to 168,594 – 189,294 MW, with production capacity reaching 252.1 – 291.5 billion kWh, equivalent to 50% of households using rooftop solar for self-production and self-consumption (for local use, without selling electricity back to the national grid)[4].
Along with that, the government is also taking actions to promote the development of rooftop solar power usage. For example, in the case of private projects (households, public offices, office buildings, etc.), the installation of rooftop solar systems for self-production and self-consumption (not for commercial purposes) is being discussed to have the construction procedures simplified as much as possible[5]. These initiatives aim to promote energy conservation and sustainability, fostering a culture of renewable energy adoption.
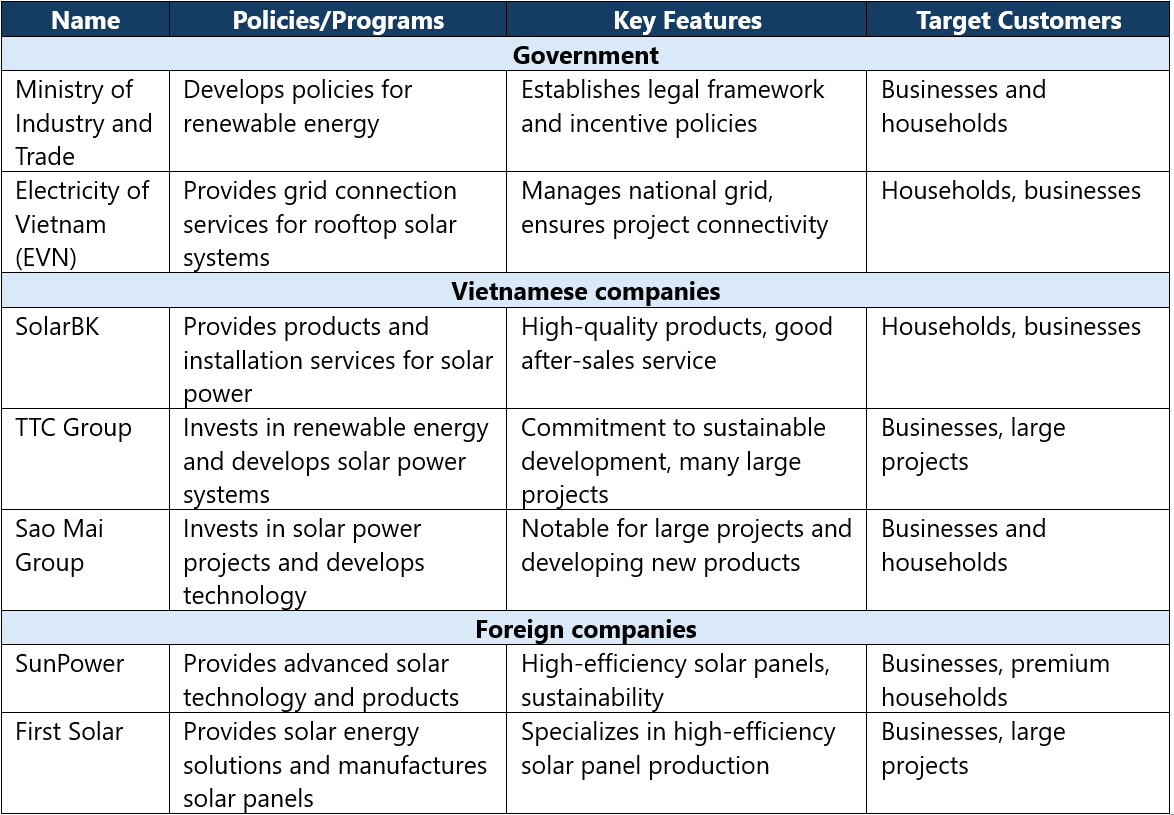
Key Players
The development of rooftop solar power in Vietnam involves a diverse range of key players, including government agencies, private companies, and financial institutions. The Ministry of Industry and Trade (MOIT) plays a central role in formulating policies and regulations governing the energy sector, while the Electricity of Vietnam (EVN) is responsible for managing the national electricity grid and facilitating the connection of rooftop solar systems.
Private companies have also emerged as significant contributors to the solar energy landscape. Local firms such as SolarBK, TTC Group, and Sao Mai Group are actively involved in the production and installation of solar panels and systems. These companies not only offer competitive pricing but also provide financing options to make rooftop solar installations more accessible to homeowners and businesses.
International firms, including major players like SunPower and First Solar, have also entered the Vietnamese market, bringing advanced technology and expertise. Their involvement has contributed to increased competition and innovation, driving down costs and improving the quality of solar products available to consumers.
The table below compares the differences in rooftop solar power provided by various parties
Source: B&Company’s synthesis
Additionally, financial institutions are crucial in supporting the growth of rooftop solar power. Banks and investment funds are increasingly offering green loans and financing options tailored to renewable energy projects. This access to capital is essential for individuals and businesses looking to invest in solar technology, further accelerating the adoption of rooftop solar power across the country.
Opportunities and Challenges
The potential for developing rooftop solar power in Vietnam is immense, presenting numerous opportunities. The growing awareness of climate change and the need for sustainable energy solutions have led to a heightened interest in renewable energy among both consumers and businesses. As energy prices continue to rise, rooftop solar power offers a viable alternative, providing long-term cost savings and energy independence. Moreover, the trend of urbanization in Vietnam creates a significant market for rooftop solar installations. As more people move to cities, the demand for electricity is expected to soar. Rooftop solar power can help alleviate pressure on the national grid, particularly during peak demand periods. Additionally, solar energy can contribute to job creation in installation, maintenance, and manufacturing sectors, fostering economic growth.
Additionally, this introduces significant potential for foreign investment. Along with support from the Government, the shift towards sustainable energy aligns with global investment trends, making Vietnam an appealing destination for foreign investors seeking to capitalize on the green energy transition.
However, several challenges must be addressed to fully realize the potential of rooftop solar power in Vietnam. One major hurdle is the lack of awareness and understanding of solar technology among consumers. Many potential users remain hesitant to invest due to misconceptions about costs, efficiency, and maintenance. Public education campaigns and outreach efforts are essential to dispel myths and encourage adoption.
Another challenge is the regulatory framework surrounding rooftop solar power. While government policies have been favorable, there are still gaps in the implementation and enforcement of these regulations. Streamlining the permitting process and ensuring clear guidelines for grid connection can help facilitate the growth of rooftop solar installations.
Additionally, the financing landscape presents obstacles for some potential users. While green loans and financing options are becoming more accessible, many small businesses and low-income households may still struggle to secure funding for solar projects. Developing innovative financing solutions, such as community solar initiatives, could help address these barriers and promote broader participation.
Conclusion
The potential for developing rooftop solar power in Vietnam is vast, driven by a combination of favorable government policies, abundant sunlight, and a growing market demand for renewable energy. With the government’s ambitious targets and continued support, the rooftop solar sector is poised for significant growth in the coming years.
However, realizing this potential requires concerted efforts to address existing challenges, including consumer awareness, regulatory frameworks, and financing options. By fostering collaboration among key stakeholders and implementing effective outreach initiatives, Vietnam can successfully harness its rooftop solar potential. This transition not only promises to enhance energy security and sustainability but also positions Vietnam as a leader in the renewable energy landscape of Southeast Asia. As the country moves towards a greener future, rooftop solar power will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping a sustainable energy ecosystem.
[1] EVN (2017). Renewable energy development in Vietnam: huge untapped potential. <Assess>
[2] VnEconomy (2023). Solar power still has a lot of potential for development. <Assess>
[3] Prime Minister (2017). Regarding the mechanism to encourage the development of solar power projects in Vietnam. <Assess>
[4] Prime Minister (2023). Approval of the National Power Development Plan for the period 2021-2030, with a vision for 2050. <Assess>
[5] Vietnam News Agency (2024). Simplifying procedures to the max to encourage the development of rooftop solar power. <Assess>
| B&Company, Inc.
The first Japanese company specializing in market research in Vietnam since 2008. We provide a wide range of services including industry reports, industry interviews, consumer surveys, business matching. Additionally, we have recently developed a database of over 900,000 companies in Vietnam, which can be used to search for partners and analyze the market. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you have any queries. info@b-company.jp + (84) 28 3910 3913 |
Read other articles