04Feb2025
Industry Reviews / Latest News & Report
Comments: No Comments.
Overview of supporting industry in Vietnam
Vietnam’s supporting industries play a pivotal role in the nation’s economic transformation, driving industrialization and modernization efforts. By bolstering the processing and manufacturing sectors, these industries significantly enhance Vietnam’s overall economic structure. Decree No. 111/2015/ND-CP[1] defines supporting industries as industries that produce raw materials, materials, components, and spare parts to supply for the production of finished products.
The manufacturing of components and spare parts (including metal, plastic, and electrical-electronic parts and components) is one of three targeted areas within the supporting industry, – alongside the supporting industries for textiles, footwear, and leather, as well as for high-tech industries. In this article, we focus on discussing the field of components, spare parts, and machinery and equipment, which has a strong connection to Japanese collaboration.
From a broad perspective, these “supporting industry” companies are part of Vietnam’s mechanical industry, which, according to the General Statistics Office (GSO), comprises approximately 30,000 enterprises. The whole sector generates a total revenue of over 1.7 quadrillion VND and provides employment for more than 1.2 million workers[2].
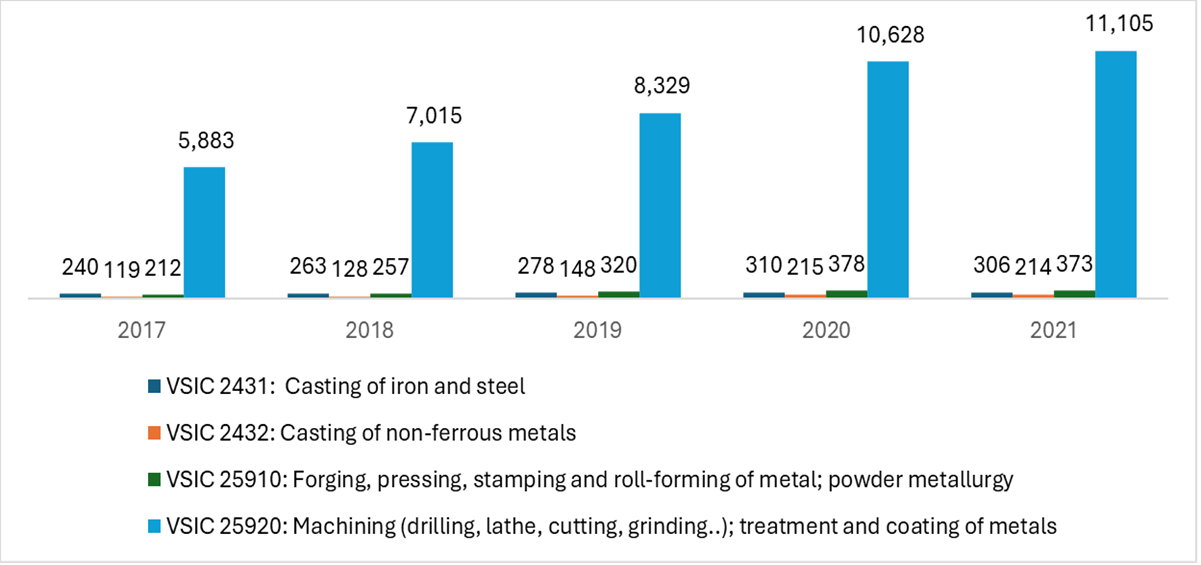
Mechanical processing is a subset of the mechanical industry that involves the fabrication and production of components, parts, or products made from metals and other materials through machining methods such as cutting, shaping, casting, forging, stamping, welding, and other mechanical treatment methods. According to statistics from B&Company’s enterprise database based on the Vietnam Standard Industrial Classification (VSIC)[3] in 2021, the number of mechanical processing companies[4] reached 11,998 companies, and total revenue reached 197,947 billion VND, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15% during the 2017-2021 period. Besides, by processing method, the number of companies operating in the fields of machining, casting, forging, and stamping tended to increase over the years from 2017- 2021.
Number of companies by processing method, period of 2017-2021
(Unit: companies)
Source: B&Company’s enterprise database
From a supply chain perspective, the Ministry of Industry and Trade (MoIT) reports that approximately 5,000 companies in Vietnam currently supply components for the automotive and mechanical industries. Of these, 70% cater to domestic manufacturers, 8% serve exporters (primarily targeting key markets such as South Korea, Japan, China, and the United States), and 17% supply to both. As a result, around 30% of Vietnamese companies within the supporting industries are integrated into global supply chains[5].
Opportunities and challenges for the development of the supporting industry
The supporting industry in Vietnam presents significant opportunities for growth, driven by a combination of strategic geographic advantages, robust government support, and foreign investment from global manufacturing leaders.
Firstly, Vietnam’s strategic location in Southeast Asia offers excellent access to major regional markets such as China, Japan, and South Korea. This geographic advantage, if combined with an efficient transportation and logistics network, will help to reduce costs and enhance market accessibility. Vietnam has emerged as an attractive destination for global giants such as Apple, Canon, LG, Samsung, Google, and Panasonic. Consequently, when these multinational corporations expand their supply chains into Vietnam, their tier-1 suppliers—such as Foxconn, Jabil, Pegatron, and Wistron—follow suit, further strengthening the country’s industrial base.
Besides, the Vietnamese government actively supports the growth of supporting industries through a range of policies, including tax incentives, financial aid, and access to specialized training programs. In addition, the government has signed multiple Free Trade Agreements (FTAs), further boosting the country’s export activities and global trade connections.
However, despite remarkable success in attracting foreign investment, Vietnam’s supporting industries continue to face significant hurdles. 88% of local companies in these industries are classified as small or medium-sized enterprises, who often struggle with limited financial and human resources. Moreover, Vietnam lacks industry-leading companies with strong market influence, and investment in research and development (R&D) as well as new product innovation remains minimal. These challenges limit the country’s ability to fully integrate into global value chains.[6] Adding to the difficulty, international companies tend to rely on well-established suppliers or firms from their home markets, leaving Vietnamese companies at a disadvantage. Weak connections with major global brands often place local businesses in a reactive position, making it difficult for them to secure favorable terms and partnerships.[7]
Opportunities for Japanese enterprises in Vietnam’s supporting industry
Japan has established itself as one of Vietnam’s most significant economic partners, playing a crucial role in the development of the country’s industrial and supporting industries through substantial investment and close collaboration. Among 143 countries and territories investing in Vietnam, Japan stands out as the third-largest investor, with around 5,300 projects totaling $74 billion in value, more than 70% of which are in the industrial sector[8].
Vietnam’s supporting industry is receiving much attention from Japanese businesses and investors. Mr. Takeo Nakajima, Chief Representative of the Japan External Trade Organization in Hanoi, emphasized Japan’s strong interest in Vietnam, stating, “Many Japanese enterprises now consider Vietnam an indispensable link in their supply chain. To further strengthen this role, Vietnam needs to focus on the extensive development of its supporting industries. A stable domestic supply of raw materials and components will enable businesses to create more flexible supply chains, reduce costs, and drive the advancement of the domestic manufacturing and processing sectors”[9].
On the other hand, according to a survey by JETRO, the localization rate of Japanese enterprises in Vietnam has increased from 28% ten years ago to 37% in 2022[10]; but the companies are facing difficulties, particularly in terms of supplier quality. Despite some companies achieving high localization rates, the need for reliable, high-quality suppliers who can offer competitive pricing remains a challenge for further progress.
In response to this situation, many Vietnamese companies in the supporting industry have expressed their commitment to meeting the high standards of their Japanese partners. These Vietnamese companies are willing to continue investing in facilities and technology to meet Japanese standards, reflecting the importance of these partnerships in driving growth and success in the industry.
Besides, the Vietnamese government has put critical effort into promoting the development of supporting industry. Recognizing that reducing costs is critical to the growth of Vietnam’s supporting industries, the government has put on initiatives such as preferential loans, tax exemptions, and unsecured guarantees to help enterprises expand production and integrate into global supply chains. The proposed amendment of Decree No. 111/2015/ND-CP aims to broaden the definition of supporting industries and offer enhanced incentives for businesses involved in essential production stages like forging and plating. It also seeks to leverage Vietnam’s free trade agreements to increase the localization of raw materials and reduce reliance on imports. Looking ahead, the Ministry of Industry and Trade is drafting the Key Industrial Law[11] to create a unified legal framework for the development of processing, manufacturing, and supporting industries.
In conclusion, Japan’s strong investment and collaboration offer significant opportunities for advancing Vietnam’s supporting industries. With government incentives and improved localization efforts, Vietnam still presents a promising direction for Japanese companies to strengthen supply chains and foster sustainable partnerships.
[1] Decree No. 111/2015/ND-CP on Development of Supporting Industry <Access>
[2] Vietnam Industry Agency (2022) Overview of Vietnam’s mechanical market in 2022 <Access>
[3] Vietnam Standard Industrial Classification (VSIC) <Access>
[4] VSIC 24310 Casting of iron and steel; VSIC 24320 Casting of non-ferrous metal; VSIC 25910 Forging, pressing, stamping, and roll-forming of metal; powder metallurgy; VSIC 25920 Machining (drilling, lathe, cutting, grinding..); treatment and coating of metals
[5] MOIT (2023): Supporting industry enterprises need to get closer to the global value chain <Access>
[6] HCMC Center for supporting industries development – CSID (2023): Where is Vietnam Supporting Industry <Access>
[7] VNEconomy (2024): For the development of support industries <Access>
[8] VNBusiness (2024): Japanese enterprises consider Vietnam a safe investment destination <Access>
[9] CafeF (2023): Developing supporting industries to attract Japanese enterprises <Access>
[10] CafeF (2023): Developing supporting industries to attract Japanese enterprises <Access>
[11] Vietnam Government Portal (2024): Proposal for the development of a Law on Key Industries <Access>
* If you wish to quote any information from this article, please kindly cite the source along with the link to the original article to respect copyright.
| B&Company
The first Japanese company specializing in market research in Vietnam since 2008. We provide a wide range of services including industry reports, industry interviews, consumer surveys, business matching. Additionally, we have recently developed a database of over 900,000 companies in Vietnam, which can be used to search for partners and analyze the market. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you have any queries. info@b-company.jp + (84) 28 3910 3913 |