244월2025
하이라이트 콘텐츠 / 업계 리뷰 / 최신 뉴스 및 보고서
댓글: 댓글 없음.
일본의 투자는 베트남 에너지 부문, 특히 재생에너지 성장을 견인하고 있습니다. 증가하는 에너지 수요로 베트남은 심각한 어려움에 직면해 있지만, 전략적 계획과 일본과의 탄탄한 협력 관계는 유망한 해결책을 제시합니다. 따라서 에너지 부문은 인프라와 지속가능한 에너지 개발을 중심으로 변혁을 맞이할 준비가 되어 있습니다.
최근 몇 년 동안 일본에서 베트남으로 투자 이동
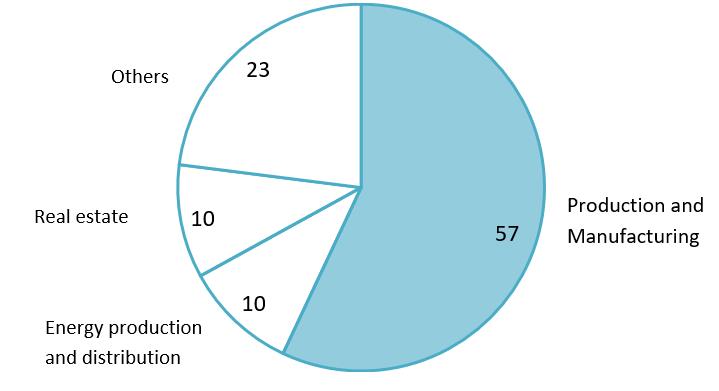
일본은 다양한 분야에서 베트남의 핵심 전략적 파트너로서 자리매김하고 있습니다. 2023년 한 해 동안 일본의 신규 FDI 등록액은 약 70억 달러에 달하며, 싱가포르에 이어 두 번째로 큰 투자국이 되었습니다.[1]2021년 기준 일본의 베트남 누적 투자액은 약 630억 달러에 달했습니다. 특히 에너지 분야는 약 70억 달러를 기록하며, 제조업 및 가공업에 이어 투자액 기준 2위를 차지했습니다.[2].
FDI from Japan to Vietnam by sector in 2021[3]
단위: 100% = 629억 달러
원천: 오사카 베트남 총영사관
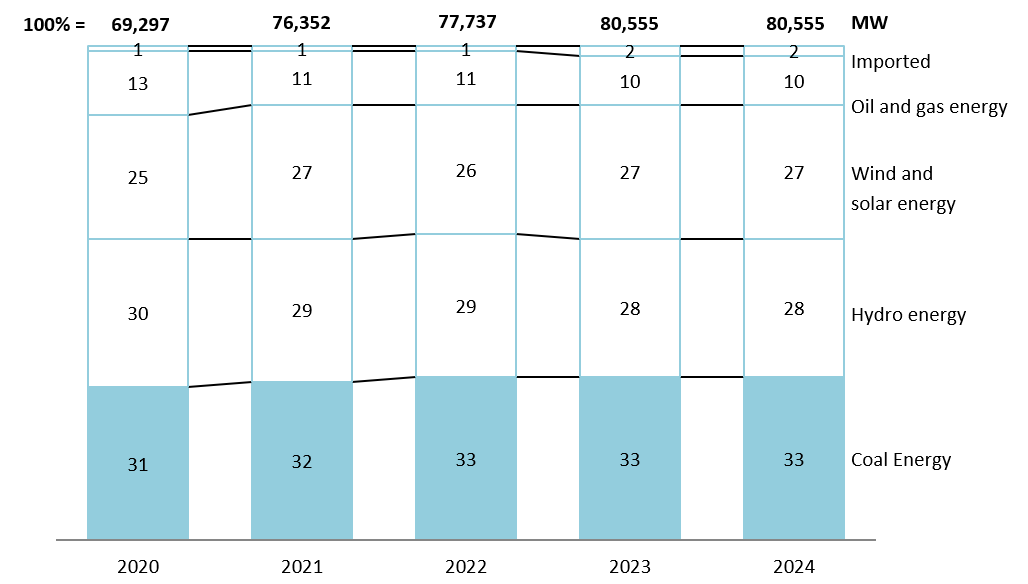
2020년부터 2024년까지 베트남의 발전 유형별 에너지 생산량
출처: 베트남 에너지 협회
전반적으로 베트남 에너지 부문은 긍정적인 성장세를 보이고 있습니다. 2024년 기준 베트남은 84,360MW의 에너지를 생산하며, 2020년부터 2024년까지 연평균 5%의 성장률을 보일 것으로 예상됩니다. 화석 연료는 여전히 가장 큰 에너지원으로, 석탄이 33%, 석유와 가스가 10%를 차지합니다. 재생 에너지가 그 뒤를 바짝 쫓고 있으며, 풍력과 태양광은 총 발전량에서 27%, 수력은 28%를 차지합니다. 이러한 분포는 2020년 이후 비교적 안정적으로 유지되었지만, 재생 에너지가 계속 성장함에 따라 향후 상당한 변화가 예상됩니다.[4].
일본의 에너지 부문 투자
베트남 에너지 부문의 성장 궤도와 함께, 일본의 베트남 에너지 부문 투자는 투자 가치와 에너지 종류 측면에서 크게 발전했습니다. 이전에는 일본의 투자 프로젝트가 주로 재생에너지에 집중되었지만, 일부 프로젝트는 화석연료 프로젝트도 포함되었으며, 1억 달러를 초과하는 프로젝트는 거의 없었습니다. 그러나 2023년 5월 베트남 정부가 전력개발계획 8(PDP8)을 수립하면서, 베트남은 재생에너지 비중을 2030년까지 50%(전력 3조 1천억 원), 2050년까지는 70%(전력 3조 1천억 원)로 확대하는 목표를 세웠습니다.[5]그 이후로 일본의 투자 가치는 크게 변화했으며, 프로젝트 규모는 200억 달러에 달했습니다.
PDP8 이전 일본 에너지 부문 투자 일부
| 프로젝트 이름 | 주요 자금원 | 투자 가치
(백만 달러) |
투자 연도 | 위치 |
| 붕앙 2 석탄화력발전소 | 일본 국제협력은행(JBIC) | 636 | 2020 | 하띤 |
| 닌투언성 육상 풍력 발전 | 일본 국제 협력기구(JICA) | 25 | 2022 | 닌투안 |
| 콕산 수력발전소 | 도쿄전력 재생에너지 | 18 | 2018 | 라오까이 |
출처: B&Company 편집
PDP8 이후 일본에서 베트남으로의 일부 투자 프로젝트
| 프로젝트 이름 | 주요 자금원 | 투자 가치
(백만 달러) |
투자 연도 | 위치 |
| B 블록 가스전 개발 | 미쓰이 석유 탐사 회사(MOECO) | 740 | 2024 | 말레이-토 추 분지 |
| 저탄소 에너지 | 일본국제협력은행 및 민간기업 | 20,000 | 2025 | 없음 |
| 닌투안 2 원자력 발전소 | 일본 국제 원자력 에너지 개발(JINED) 및 일본 원자력기구(JAEA) | 건설 지원 | 2036년 – 2040년 | 닌투안 |
| 부유식 LNG 수입 터미널 및 천연가스 발전소 | 도쿄가스앤큐덴 | 없음 | 2029 | 타이빈 |
출처: B&Company 편집
투자 이유
베트남 경제의 맥락에서 GDP가 1% 성장할 때마다 에너지 소비량은 1.5% 증가합니다. 따라서 기획투자부의 성장 전망에 따르면 2025년 전력 소비량은 12%에서 13%까지 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다.[6]그러나 평균 전력 생산량 증가율이 5%에 불과하여 증가하는 수요를 충족하는 데 어려움을 겪을 것으로 예상됩니다. 따라서 2025년부터 재생에너지 시장 투자자를 지원하기 위한 다양한 정책이 도입되었습니다.
에너지 부문 지원을 위한 정부 이니셔티브
| 결정 | 발행일 | 정책 이름 | 재생에너지 활성화를 위한 조건 |
| 법령 제58/2025/NĐ-CP호 | 2025년 3월 | 재생에너지 및 신에너지 전기개발에 관한 전기법 일부 조항에 대한 세부 설명 | Wind energy
· 공사기간 중 해역사용료 최대 3년간 면제, 이후 12년간 50% 감면 · 기본공사기간 중 토지사용료 및 임대료 면제(단, 착공일로부터 3년을 초과할 수 없음) · 대출원금상환기간 중 최소 80% 발전계약 체결, 최장 15년 이내 옥상 태양열 에너지 · 100kW 미만의 전기용량을 가진 개인 및 가구는 사업자등록이 필요하지 않습니다. · 총 발전량의 20%를 초과하지 않는 범위 내에서 잉여 전력을 판매할 수 있음 재생에너지 및 신에너지 · 공사기간 중 해역사용료 최대 3년간 면제, 이후 9년간 50% 감면 · 기본공사기간 중 토지사용료 및 임대료 면제(단, 착공일로부터 3년을 초과할 수 없음) · 대출원금상환기간 중 최소 70% 발전계약, 최대 12년 이내 |
| 전력개발계획 8차 개정 | 2월
2025 |
전력개발계획 8호 개정안 | 에너지 개발
· 국가 경제 전망에 부합하는 에너지 부문 5대 발전 시나리오 제시 · 2030년까지 최대 10,000MW의 에너지 수출 목표 설정 국가 에너지 그리드 · 2030년까지 500kV 송전망이 널리 구축될 예정입니다. · 신뢰성 확보를 위한 220kV 자체 운영 그리드 구축 |
| 결정 번호 245/QĐ-TTg | 2월
2025 |
2030년까지 원자력 발전 및 응용 계획, 2050년까지의 비전 | 의료, 농업, 산업 등 다양한 분야에 핵 에너지를 보다 광범위하게 통합하기 위한 핵심 목표를 설정합니다. |
출처: 베트남 정부 포털
강력한 정부 지원과 개정된 PDP8에 명시된 명확하게 정의된 개발 목표에 따라 베트남의 에너지 부문은 상당한 성장을 경험할 것으로 예상됩니다. 특히, 국내외 투자자의 관심이 높아지고 있는 재생 에너지 분야에서 성장세가 두드러질 것으로 예상됩니다.
베트남에 대한 일본 투자자들의 전망과 과제
일본 투자자는 몇 가지 주요 이점에 힘입어 베트남 에너지 시장에 투자할 수 있는 수많은 기회를 갖고 있습니다.
첫째, 일본은 베트남의 최대 공적개발원조(ODA) 제공국이다.[7] 그리고 아시아 제로 배출 공동체(AZEC)의 회원입니다.[8]결과적으로 재생에너지 부문 투자 프로젝트는 상당한 지원을 받을 수 있는 유리한 위치에 있습니다. 둘째, 베트남의 LNG 에너지 프로젝트 완료 목표는 2030년으로 설정되어 있습니다. 그러나 현재 16개 프로젝트 중 2개만 완료되었으며, 나머지 프로젝트들은 투자 유치에 어려움을 겪고 있습니다. 이는 특히 LNG 부문에서 베트남 에너지 시장 진출을 모색하는 일본 기업들에게 귀중한 기회를 제공합니다.[9]. 마지막으로, 해외에서 사업을 운영하는 일본 기업에 대한 JETRO 보고서에 따르면, 베트남에 있는 832개 일본 기업 중 62%의 응답자가 투자 환경 측면에서 성장 잠재력이 있는 확장 가능한 시장으로 베트남을 평가했습니다.[10].
그러나 이러한 유망한 전망에도 불구하고 몇 가지 과제가 여전히 남아 있습니다. 전력 구매 계약(PPA)은 복잡하고 일관성이 부족할 수 있습니다. 많은 외국인 투자자들은 베트남의 법률 및 행정 절차의 투명성과 예측 가능성 부족에 대해 우려를 표명해 왔습니다.[11]또한 현재 국가 전력망의 한계(특히 재생 에너지 잠재력이 높은 지역)로 인해 태양광 및 풍력 프로젝트가 축소되어 투자 수익에 영향을 미치고 있습니다.[12].
결론
일본의 베트남 에너지 부문 투자는 지속가능한 개발과 에너지 안보에 대한 강력한 의지를 반영합니다. 베트남은 재생에너지 시장에서 상당한 기회를 제공하지만, 일본 투자자들은 규제 불확실성, 전력망 제한, 그리고 자금 조달의 어려움을 헤쳐나가야 합니다. 이러한 과제를 해결함으로써 일본과 베트남은 이 지역의 더 깨끗하고 회복력 있는 에너지 미래를 선도하는 데 주도적인 역할을 할 수 있습니다.
[1] 베트남 통계청(2024). 2023년 베트남 신규 등록 외국인직접투자(FDI)입장>
[2]오사카 베트남 총독부(2021)와 협의. 일본의 베트남 투자입장>
[3] 사용 가능한 최신 데이터
[4] 베트남 에너지 온라인(2025). 2024년 베트남 에너지 개요입장>
[5] 베트남 정부 포털(2023). 결정 번호 500/QD-TTg: 2021-2030년 국가 전력 개발 계획 승인(2050년 비전 포함)입장>
[6] VnBusiness (2024). 2025년 베트남 에너지 소비 전망입장>
[7] 베트남 기획투자부(2024). 베트남-일본, 새 시대 공동 이니셔티브 중간 이행 검토입장>
[8] 일본 경제산업성(2024). 아시아 제로 배출 커뮤니티 회원입장>
[9] 베트남 산업통상부(2025). 전력개발계획 8(PDP8) 개정입장>
[10] 일본무역진흥기구(2024). 2024년 해외 진출 일본 기업 경영실태 조사입장>
[11] 로이터(2025). 베트남 태양광 및 풍력 투자 1조 4천억 달러 이상 위험에 처해입장>
[12] 펄크럼(2024). 베트남 재생에너지 사가의 예상치 못한 반전입장>
* 본 기사의 내용을 인용하고자 하시는 경우, 저작권을 존중하여 출처와 원 기사의 링크를 함께 명시해 주시기 바랍니다.
| 비앤컴퍼니
2008년부터 베트남에서 시장 조사를 전문으로 하는 최초의 일본 기업입니다. 업계 보고서, 업계 인터뷰, 소비자 설문 조사, 비즈니스 매칭을 포함한 광범위한 서비스를 제공합니다. 또한, 최근 베트남에서 900,000개 이상의 기업에 대한 데이터베이스를 개발하여 파트너를 검색하고 시장을 분석하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다. 문의사항이 있으시면 언제든지 문의해주세요. info@b-company.jp + (84) 28 3910 3913 |